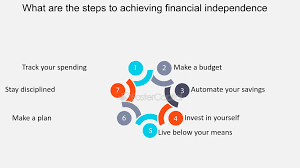
Managing personal finances effectively is one of the most important skills for achieving long-term financial success and stability. Whether you’re a beginner just starting to explore financial concepts or someone looking to refine your existing knowledge, mastering personal finance is crucial for building wealth, managing debt, and securing a financially independent future. This comprehensive guide will walk you through essential financial principles such as budgeting, credit management, debt reduction, investing, and retirement planning.
1. The Importance of Budgeting: Take Control of Your Financial Life
What is Budgeting?
Budgeting is the practice of creating a plan that allows you to allocate your income toward expenses, savings, and investments. Essentially, a budget helps you track your income and expenses, ensuring that you don’t overspend while meeting your financial goals. By following a structured budgeting plan, you are more likely to achieve your financial objectives and avoid falling into debt.
Why Budgeting Matters
Budgeting is critical because it helps you gain control over your finances. Without a budget, it’s easy to spend without awareness, which can lead to financial stress and missed opportunities for saving and investing. A budget allows you to identify areas where you can cut back and ensures that your financial priorities, such as saving for retirement or building an emergency fund, are met.
Steps to Create a Budget
- Track Your Income: Start by calculating your monthly income from all sources (salary, side hustles, etc.).
- Categorize Your Expenses: Split your expenses into fixed expenses (rent, utilities, loan payments) and variable expenses (groceries, entertainment, dining out).
- Set Goals: Decide how much you want to save each month and set aside money for any financial goals such as vacation funds or saving for a home down payment.
- Adjust and Monitor: After evaluating your income and expenses, adjust your spending where necessary. Aim to allocate any surplus toward savings or paying off debt.
2. Credit Management: Building and Maintaining a Strong Credit Score
What is Credit?
Credit refers to the ability to borrow money, usually from a financial institution or lender, with the understanding that you will repay it at a later date, typically with interest. Access to credit is vital in our financial lives, especially when making large purchases like buying a house or car.
What is a Credit Score?
A credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness. It is determined by your credit history, including factors like your payment history, outstanding debts, credit utilization, length of credit history, and types of credit used. Credit scores generally range from 300 to 850, with a higher score reflecting a stronger credit history.
Why Your Credit Score is Crucial
Your credit score affects your ability to secure loans, obtain credit cards, and even rent an apartment. A higher score typically results in lower interest rates, while a lower score may make it difficult to qualify for loans or could result in higher interest rates. Maintaining a good credit score can save you money in the long run and improve your financial options.
Tips to Improve Your Credit Score
- Pay Your Bills on Time: Timely payments are one of the most important factors in improving your score. Set reminders or automate payments to avoid late fees.
- Keep Your Credit Utilization Low: Aim to keep your credit card balances below 30% of your credit limit to maintain a healthy credit score.
- Limit Hard Inquiries: Only apply for credit when necessary, as multiple credit inquiries in a short period can negatively impact your score.
- Monitor Your Credit Report: Regularly check your credit report for errors and dispute any inaccuracies that could affect your score.
3. Debt Management: How to Get Out of Debt and Stay Debt-Free
What is Debt?
Debt occurs when you borrow money from a lender with the intention of repaying it later, usually with interest. While some forms of debt, such as mortgages or student loans, can be considered “good debt,” high-interest debt, like credit card debt, can quickly become overwhelming and detrimental to your financial well-being.
Why Debt Management is Essential
Debt management is vital for maintaining a healthy financial life. When debt piles up, it can lead to financial stress, high-interest costs, and long-term financial struggles. Managing your debt effectively allows you to regain control over your finances and set yourself up for future success, including saving and investing.
Steps to Effectively Manage Debt
- List All Debts: Write down all your outstanding debts, including the balances, interest rates, and minimum payments.
- Prioritize Debt Repayment: Focus on paying off high-interest debt first, such as credit card debt. Consider using methods like the snowball or avalanche debt repayment strategies.
- Consider Debt Consolidation: If you have multiple high-interest debts, consolidating them into a single loan with a lower interest rate can simplify payments and help you save money on interest.
- Avoid Accruing More Debt: Stop using credit cards or taking out loans unless necessary. Avoid impulse purchases and stick to your budget.
- Seek Professional Help if Necessary: If your debt feels overwhelming, consider working with a financial advisor or credit counselor who can help you create a repayment plan.
4. Saving for the Future: Building an Emergency Fund and More
What is Saving?
Saving refers to setting aside a portion of your income for future use, usually in a savings account or other low-risk financial instruments. Saving is essential for covering emergencies, future expenses, and for building wealth over time.
Why Saving is Important
Having a solid savings plan is essential for financial security. Emergencies and unexpected expenses, such as medical bills or car repairs, can arise at any time. Having an emergency fund allows you to cover these costs without relying on credit cards or loans. Additionally, saving for long-term goals, like retirement or purchasing a home, provides a sense of financial stability.
How to Start Saving
- Set Savings Goals: Identify short-term and long-term savings goals, such as building an emergency fund, saving for a vacation, or contributing to retirement.
- Open a Separate Savings Account: Consider opening a high-yield savings account to earn interest while keeping your savings separate from your everyday spending account.
- Automate Your Savings: Set up automatic transfers to your savings account to ensure that saving is a consistent habit.
- Start Small: Begin by saving small amounts, even $25 to $50 per month, and gradually increase your savings as your income allows.
5. Investing: Growing Your Wealth Over Time
Why Invest?
Investing is the process of putting your money into assets, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, with the goal of generating returns over time. Unlike saving, which primarily preserves your money, investing allows your money to grow and potentially outpace inflation.
Types of Investments
- Stocks: Owning a share in a company. Stocks offer the potential for high returns but also carry higher risks.
- Bonds: Lending money to governments or corporations in exchange for regular interest payments. Bonds tend to be safer than stocks but offer lower returns.
- Mutual Funds & ETFs: Pooled investment vehicles that allow you to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets.
- Real Estate: Investing in property that can generate rental income or appreciate in value over time.
How to Get Started with Investing
- Start Early: The earlier you begin investing, the more time your money has to grow through the power of compounding.
- Diversify Your Investments: Spread your investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) to reduce risk.
- Choose Low-Cost Investment Vehicles: Consider investing in low-cost mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that provide broad market exposure with minimal fees.
- Review and Rebalance: Regularly review your portfolio and make adjustments based on your risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals.
6. Retirement Planning: Securing Your Financial Future
Why is Retirement Planning Important?
Retirement planning is the process of saving and investing money to ensure that you can live comfortably once you stop working. Starting early is key to building a substantial nest egg for retirement. If you wait too long, you may find it difficult to accumulate enough funds to support your lifestyle in your later years.
Retirement Accounts
- 401(k): An employer-sponsored retirement account that allows you to contribute a portion of your salary on a tax-deferred basis. Many employers also offer matching contributions.
- IRA (Individual Retirement Account): A personal retirement account that provides tax benefits. There are two main types: Traditional IRAs (tax-deferred) and Roth IRAs (tax-free withdrawals).
- Roth IRA: A retirement account where contributions are made with after-tax dollars, and qualified withdrawals are tax-free.
How Much Should You Save for Retirement?
Most experts recommend saving at least 15% of your income each year for retirement. The earlier you start, the less you will need to save each month, thanks to the power of compounding.
Steps to Begin Retirement Planning
- Estimate Retirement Expenses: Consider your current living expenses and think about how they might change during retirement (e.g., healthcare, travel, hobbies).
- Contribute to Retirement Accounts: Take full advantage of any employer-sponsored retirement plans and open an IRA if you haven’t already.
- Maximize Contributions: Try to contribute the maximum allowed to your retirement accounts, especially if your employer offers matching contributions.
- Review Your Investments: Ensure your investment strategy aligns with your retirement goals and risk tolerance. As you near retirement, consider shifting to lower-risk investments.
Conclusion
Mastering personal finance is an ongoing process that requires time, discipline, and informed decision-making. By learning to budget effectively, manage your credit, reduce debt, save for the future, invest wisely, and plan for retirement, you can take control of your financial future and achieve long-term success. Start